For the past several years, digital transformation, commonly referred to as DX, has been considered a matter of survival rather than innovation. Companies believed that moving systems online and building a digital infrastructure for storing and managing data signaled meaningful progress.
But the rise of generative AI has changed the competitive landscape entirely. The question is no longer whether an organization is digital. The real question is how effectively a company can use AI to redesign the way it operates.
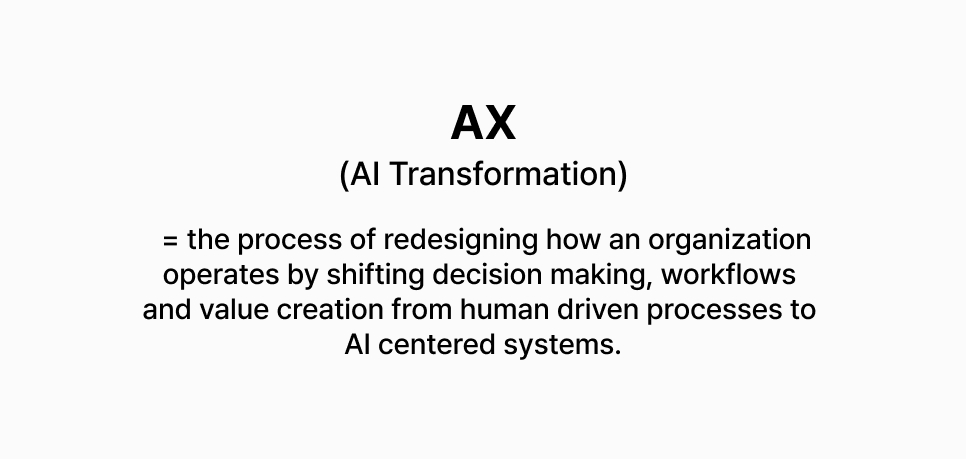
This is where AX, also known as AI Transformation, enters the picture. AX goes beyond implementing a single technology. It represents a company-wide shift in how people work, how decisions are made, and how processes are structured. This article walks through what AX means, why it matters now, and how companies are already applying it. It also provides a practical guide for organizations preparing to begin their AX journey.
What exactly is AX?
AX refers to Artificial Intelligence Transformation. It represents the stage that follows digital transformation. While digital transformation focused on computerizing business processes and building online and mobile systems, AX focuses on embedding AI into those digital environments to enhance decision making, operations, and customer experience.
| Category | DX Era | AX Era |
|---|---|---|
| Work Ownership | People operate the system | AI analyzes and proposes, people review and approve |
| Data Usage | Focused on storing and retrieving data | Focused on prediction and decision making |
| Objective | Improving efficiency | Company wide intelligence and business model innovation |
| Organizational Structure | Process centered | Algorithm centered |
Industry research and expert commentary commonly define AX as a shift toward AI centered work. In the past, employees directly manipulated systems, interpreted data, and made decisions on their own. In the AX era, AI analyzes the data, identifies patterns, and presents multiple recommendations. People then review, adjust, and approve the final output.
Therefore, AX is not the adoption of one or two AI tools. It is a redesign of how responsibilities are divided between people and AI. Employees move away from repetitive tasks, and AI handles large scale analysis and prediction. The result is an organization that operates with greater speed and intelligence.

Why AX Matters Now
AX does not suddenly appear. It reflects five to seven years of accumulated changes. The reasons AX has become especially important include the following.
1. Expansion of AI capabilities
Earlier AI handled narrow and limited tasks but generative AI now writes reports, drafts strategies, responds to customers, automates documents and even produces code. As these capabilities expanded, AI shifted from a simple support tool to a system that can actively execute work and participate in decision making.
2. Increased complexity of the business environment
Companies must manage volatile supply chains, shifting customer behavior, unpredictable demand, growing regulatory pressure, and real time security risks. With so many variables changing simultaneously, humans alone cannot monitor or interpret everything, making AI driven prediction and automated decision support essential.
3. Persistent talent shortages and rising labor costs
Organizations continue to face difficulty securing the talent needed for increasingly complex work while compensation, benefits, and training costs keep rising. This gap creates a stronger need for AI systems that understand context, support judgment based tasks, and reduce the burden on overstretched teams.
4. The need to fully utilize DX infrastructure
Most companies already have ERP, CRM, and MES systems, but many still struggle to turn the data inside these systems into meaningful business insight. AX allows organizations to activate this existing digital infrastructure by using AI to interpret data and convert it into practical decision making power.
Key areas where AX is applied in practice
AX is gaining the fastest traction in four major business domains. These include customer experience, manufacturing and logistics, finance and security, and HR and management. In each area, AI is not simply improving convenience. It is reshaping the way organizations operate. The following explains how AX is applied in each area.

1. Customer Experience and Marketing
In this field, AI interprets customer behavior in real time and creates personalized interactions. Global companies no longer focus on deciding which employee will serve which customer. Most first line customer contact is now handled by AI.
Below are examples of how AX is used in practice.
- Automatically reorganized UI for each customer
Online platforms no longer present a single identical screen. They configure an interface optimized for each customer in real time based on price sensitivity, preferred brands, recent interests, and browsing behavior. - AI based consultation and reservation automation
AI chatbots provide consistent, high quality service around the clock regardless of company size. - Sophisticated customer segmentation and automated campaign execution
AI divides customer groups into hundreds of micro segments and automatically executes appropriate messages and promotions.
As these examples show, many first contact points between companies and customers are already supported by AI rather than humans. These changes go beyond efficiency improvements and turn customer experience into a core competitive advantage.
2. Manufacturing, supply chain, and logistics
Global manufacturers are moving away from a model where humans manually determine process conditions.
AI now analyzes equipment data in real time and autonomously adjusts process parameters while detecting abnormal patterns that could cause quality deviations.
Below are real AX cases in this domain.

1) AI predictive maintenance system at the BMW Group Regensburg plant
BMW introduced an AI centered maintenance model that monitors equipment conditions in real time and prevents unexpected failures.
BMW introduced an AI centered maintenance model that monitors equipment conditions in real time and prevents unexpected failures.
- What changed
- AI replaced manual inspection and identifies early warning signs
- Real time monitoring reduces unplanned downtime
- Maintenance decisions follow predictive insights
- Impact
- More than five hundred minutes of annual assembly line downtime prevented
- Improved operational stability across production lines
- Lower maintenance related costs and reduced risk of failure

2) DHL logistics automation and management optimization using AI and robotics
DHL incorporated AI and robotics into warehouse, distribution, and delivery processes to streamline logistics operations.
- What changed
- Robots took over repetitive warehouse and sorting tasks
- AI optimized process flow and resource allocation
- Employees shifted toward oversight and higher value roles
- Impact
- Faster and more accurate logistics processing
- Reduced operating costs and lower labor burden
- Improved worker safety and better working conditions
These cases demonstrate that global manufacturers are already adopting AI driven process control. As a result, work efficiency increases, and both cost and processing time are significantly reduced.

3. Finance and security
In the financial industry, AX is becoming essential infrastructure.
AI performs fraud detection, real time transaction analysis, customer consultation, and risk evaluation faster and more accurately than traditional methods.
- Danske Bank’s credit card and payment fraud detection system
Danske Bank adopted a deep learning model to strengthen fraud detection across credit card and payment transactions.
- What changed
- AI analyzes transaction histories and user behavior patterns
- Fraud likelihood is evaluated more precisely than with rule based methods
- Risk alerts are generated in real time for analyst review
- Impact
- Significant reduction in unnecessary false positives
- Improved fraud detection sensitivity and accuracy
- Lower manual monitoring burden and higher operational efficiency
- The model became a reference point for many global financial institutions
These examples show that AX is no longer an experimental concept but a practical operating model that is reshaping how companies work across industries. As AI takes on more analytical and operational responsibilities, organizations gain greater speed, accuracy, and resilience. This momentum will only strengthen as more companies move toward AI centered processes.
Security and Governance Requirements for AX
AX expands how data is collected, accessed, and used, which naturally increases the need for stronger security, privacy protection, and clear accountability. To adopt AX responsibly, companies should prepare for the following areas in advance.
– Data security and privacy
Organizations must first decide which data can be used for AI training and inference and which data must remain restricted. When working with external LLM APIs or cloud based services, it is essential to specify where the data will be stored, how long it will be retained, and whether the provider can learn from it. These conditions should be set clearly from the contract stage to avoid later risks.
– AI security
AI systems must be protected from unintended behavior triggered by harmful prompts or external interference. Companies should establish safeguards that ensure critical actions, including financial approvals or policy modifications, cannot be completed by AI without human oversight. This reduces the possibility of operational disruption and ensures that AI works within defined boundaries.
– Regulatory compliance and accountability
Highly regulated industries such as finance, healthcare, and the public sector require an even stronger governance framework. AI outputs must be explainable and auditable so that organizations can demonstrate how decisions were made. Clear lines of responsibility must also be defined so it is always understood who holds the final authority when AI contributes to decision making.
Leading companies treat these areas as part of the foundation for AX. They involve legal, compliance, and security teams early to ensure that AI adoption strengthens, rather than complicates, the organization’s overall governance structure.

Step by Step Roadmap for Beginning AX
Below is a simplified roadmap that highlights only the essential actions companies need when starting AX.
1) Step one: Identify AX priority areas
Begin by selecting a small number of high value use cases.
Look for processes with repetitive tasks, accessible data, or frequent customer pain points, as these areas typically show the fastest impact from AX.
2) Step two: Begin with small pilots
Start with limited pilots so the organization can quickly test and measure AX.
Examples include:
- AI customer service for a specific inquiry category such as delivery questions
- Automated meeting notes and report generation
- AI assisted job descriptions and interview question creation
Evaluate pilots based on reduced time, fewer errors, and improved response quality.
3) Step three: Build the platform and data foundation
Once pilots succeed, establish basic data pipelines and a shared AI platform for model access, logging, and governance.
This foundation ensures new AX use cases can be added safely and consistently.
4) Step four: Scale AX and redesign organizational structures
As AX expands, create teams or roles dedicated to managing AI initiatives and clarify which responsibilities belong to humans versus AI.
AX becomes a long term transformation, not a short project, and requires continuous adjustment over multiple years.
Conclusion
DX built the digital foundation for modern organizations, but AX determines how companies actually operate within that foundation. AX is not simply about adding AI. It reshapes how decisions are made, how data is used, and how people and AI work together. As AI driven operations become standard across industries, AX will be a critical driver of long term competitiveness.
For companies preparing to begin this transition or seeking practical guidance from experienced practitioners, Liahnson & Company can connect you with the right expert within twenty four hours.

Reference
https://blog.medianavi.kr/2025-04-15-Status-and-future-of-Global-Logistics-with-AI-and-robotics
https://www.elastic.co/blog/financial-services-ai-fraud-detection
https://blog.naver.com/cooconportal/223566327558
https://www.igloo.co.kr/security-information/보안-101-인공지능-전환ax이란-무엇인가요

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.