The semiconductor industry is in a constant race to produce chips that are smaller, faster, and more precise each year. At the center of this race lies the CMP (Chemical Mechanical Polishing) process, which polishes the wafer surface down to the atomic level to achieve a perfectly flat finish. But no matter how sophisticated this process may be, if the polishing pad is unstable, the entire system’s quality inevitably collapses.
This is why CMP pad conditioners are so critical. Behind what may look like a simple surface management tool lies highly intricate and precise technology that sustains the yield and consistency of cutting-edge semiconductor manufacturing. What was once regarded as a consumable accessory has now evolved into a core enabler of smart semiconductor production, integrating advances in AI, sensors, and sustainability.

What is a CMP Pad Conditioner?
CMP, or Chemical Mechanical Polishing, is a key process in semiconductor and display manufacturing that makes wafer surfaces smooth and even. If this step isn’t precise, the wafer surface can become uneven, which leads to chip malfunctions or higher defect rates. The polishing pad used in CMP gradually wears down and builds up slurry residue and debris. When that happens, polishing efficiency and quality drop. A pad conditioner keeps the pad in good shape by restoring the surface, extending its life, and making sure the polishing stays consistent.
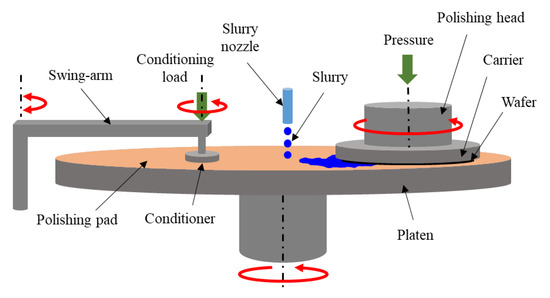
How Does It Work?
A pad conditioner is typically a disk or brush embedded with diamond particles. As it rotates against the pad, it gently scrapes away residue, removes contaminants, and restores a uniform texture. It works a lot like brushing your teeth. Without regular cleaning, buildup accumulates and overall performance drops. In fabs that process hundreds of wafers each day, conditioning is what makes sure every wafer is polished with the same level of precision.

Main Types and Manufacturing Methods
CMP pad conditioners come in several forms, each optimized for different needs:
- Disk type: Metal disks embedded with fine diamond particles for high durability and precision conditioning.
- Brush type: High-strength bristles, often made from silicone-based materials, for more gentle cleaning action.
- Micro-patterned disks: Surfaces etched with dots, grids, or lines to optimize slurry distribution and surface roughness control.
They are fabricated using a variety of advanced methods:
- Electroplating: A cost-effective process that bonds diamond particles with metals such as nickel, though durability can be limited.
- Brazing: Fuses diamond with metal at high temperatures for superior strength and longer service life.
- Sintering: Uses extreme pressure and heat to create high-performance tools suitable for advanced manufacturing.
- CVD (Chemical Vapor Deposition): Deposits thin diamond films at the nanoscale, making it ideal for next-generation processes at 5nm and below.

Applications Beyond Semiconductors
Although vital to semiconductor fabs, CMP pad conditioners are also indispensable across other precision industries. They’re deployed in polishing silicon, GaAs, and SiC wafers; in producing OLED and LCD panels; in MEMS and sensor manufacturing; and even in high-precision medical devices and automotive radar systems. When pad conditioning is neglected, defect rates can spike and entire wafer batches may be scrapped. Conversely, accurate and timely conditioning directly boosts yield and ensures stable mass production.
Real-world results emphasize their value. At Samsung Electronics, optimized CMP pad conditioning reduced wafer defect rates by more than 20%, while LG Display achieved major improvements in OLED panel yields by deploying advanced conditioners. These case studies highlight just how critical these solutions are for both semiconductors and displays.
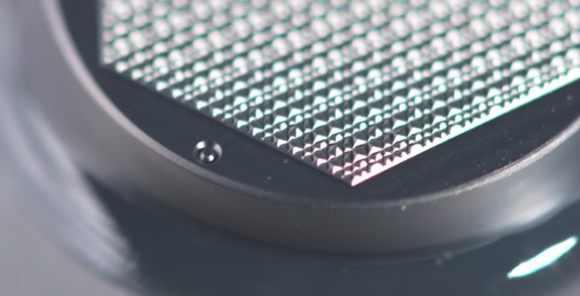
Leading Companies in the Market
The global CMP pad conditioner market was valued at about USD 320 million in 2024, and several key players dominate the landscape:
- 3M (USA): A long-time pioneer with over 25 years of leadership, 3M offers a wide product lineup—from diamond disks to patterned conditioners—and actively drives eco-friendly and smart manufacturing initiatives.
- Kinik Company (Taiwan): Rapidly strengthening its presence in Asia, with strong supply chains for major foundries and memory makers. Known for innovations in micro-patterning and CVD technology.
- Shinhan Diamond (Korea): Leveraging strong diamond materials expertise, the company has become a strategic partner for Samsung and other global semiconductor manufacturers.
- Saesol (Korea): Gaining ground with cost-competitive yet high-quality products, while focusing on brazing, CVD, and localized service strategies.
- Entegris (USA): Specializes in high-durability, automation-friendly conditioners, widely trusted by leading fabs in North America and Europe.
- Nippon Steel / NS Medres (Japan): Builds on Japan’s strong materials heritage, renowned for reliability and advanced diamond bonding technology.
Historically, US and Japanese firms held the strongest positions, but Korean, Taiwanese, and Chinese companies are expanding with competitive pricing, rapid local support, and innovative features.
Market Forecast and Emerging Trends
The CMP pad conditioner market is expected to grow steadily alongside advancements in semiconductors and displays. New demands will arise from areas such as advanced nodes, 3D ICs, automotive SiC solutions, and glass-based packaging. On the technical front, we are seeing greater adoption of CVD diamond, low-VOC eco-friendly materials, and IoT-enabled real-time monitoring. Sustainability pressures and ESG requirements will further accelerate the need for resource-efficient conditioners.
Beyond hardware, integrated solutions that combine conditioning tools with software, automation, and process optimization are becoming increasingly important. Global leaders are investing in R&D, patents, and partnerships, while mid-sized competitors are carving out opportunities with localization, agility, and price competitiveness.
Conclusion
CMP pad conditioners may not be the most visible element of semiconductor manufacturing, but they are indispensable in ensuring quality, yield, and reliability. As industries move toward more advanced and sustainable production, these tools will continue to evolve from consumables into strategic enablers of smart manufacturing. The future of CMP pad conditioning will be defined by innovation, environmental responsibility, and customer-focused solutions, making it a quiet yet powerful force in the semiconductor ecosystem.

Reference
https://patents.google.com/patent/US20060172662A1/en
https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com/blog/top-7-trends-in-cmp-pad-conditioners
https://www.businessresearchinsights.com/market-reports/cmp-pad-conditioners-market-108568
https://www.marketreportanalytics.com/reports/cmp-pad-conditioners-380941
https://www.verifiedmarketreports.com/ko/product/cmp-pad-conditioners-sales-market-size-and-forecast
https://www.marketreportanalytics.com/reports/cmp-pad-conditioners-380941#summary
Leave a Reply