The criteria people use to evaluate cars are changing at a fundamental level. Vehicle performance and fuel efficiency once dominated purchase decisions. Today, buyers increasingly focus on whether a car can update itself remotely, connect seamlessly with smartphones and unlock new capabilities through software based services. The car is no longer perceived as a finished product at the point of sale. It is becoming a digital system that continues to evolve throughout its life.
This shift is driven by Connected Car Service, commonly referred to as CCS. By keeping vehicles continuously connected to digital networks, CCS is reshaping customer expectations, competitive dynamics, and revenue models across the automotive industry.
This article examines how CCS emerged, what capabilities it enables, how leading companies are applying it, and why it is becoming a core foundation of future mobility.

From Standalone Machines to Connected Systems
The simplest way to define CCS is to think of a car that is always connected to the Internet. Modern vehicles are equipped with communication modules and software that allow them to exchange data in real time with the cloud, smartphone applications, other vehicles and road infrastructure. This constant connectivity enables vehicles to interact continuously with external systems and digital services.
| 🔎 What Is Connected Car Service(CCS)?
| Connected Car Service(CCS) is a system that connects vehicles to the Internet and continuously provides digital services such as safety functions, vehicle management, navigation, infotainment, payment and subscription services and over the air software updates. Through this structure, the car evolves into a digital service platform whose functions and user experience expand over time rather than remaining fixed at the point of purchase. |
Thanks to CCS, drivers can start their cars remotely from home, check whether doors are locked after parking and receive route guidance that automatically adjusts to avoid traffic congestion. These capabilities are no longer limited to a small number of luxury vehicles. They are becoming a standard part of the modern driving experience.
Why Connected Car Service Became Inevitable
Software Is Redefining the Vehicle
Modern vehicles contain an unprecedented volume of software. Driving dynamics, energy efficiency, safety systems, and user interfaces are now governed primarily by code rather than mechanical components. This shift has led to the concept of the software defined vehicle.
In a software defined environment, vehicle capabilities do not remain fixed after delivery. Over the air updates allow manufacturers to enhance performance, add features, and refine user experiences continuously. CCS serves as the mechanism that enables these updates to reach drivers in real world conditions.
Connectivity Became Ubiquitous
Advances in mobile networks, cloud infrastructure, and IoT technologies have made constant connectivity both feasible and economical. Vehicles now operate as connected nodes within digital networks rather than standalone machines. This connectivity allows cars to interact with external systems continuously and intelligently.
Data Became a Strategic Asset
Vehicles generate vast quantities of data related to location, speed, braking behavior, energy consumption, and component health. When leveraged effectively, this data enables services such as predictive maintenance, personalized insurance models, safety alerts, and optimized electric vehicle charging. CCS provides the foundation that allows data to be transformed into actionable services.

The Six Core Service Areas of CCS
Connected Car Service is not a single feature. It is an integrated capability stack that supports multiple service domains working together.
1) Safety and Driving Assistance
When a vehicle detects an accident or hazardous situation, it can automatically transmit location and vehicle data to support emergency response. Cars can also receive advance warnings about road hazards and accidents from other vehicles or infrastructure. This extends safety beyond onboard sensors by leveraging connectivity.
2) Vehicle Health Monitoring and Maintenance
Vehicles continuously collect data on battery and fuel levels, tire pressure, and diagnostic codes. CCS visualizes this information and notifies drivers when maintenance is needed. Increasingly, predictive analytics are used to identify potential failures before they occur.
3) Navigation, Traffic and Parking
Routes are optimized in real time based on traffic and accident data. For electric vehicles, navigation systems consider battery level, charging station locations and congestion. Parking availability and pricing are also integrated, creating a seamless end to end mobility experience.
4) Infotainment and Personalization
Music, audio content, and voice assistants are delivered directly to the vehicle. Driver preferences and settings are stored in cloud profiles so the same experience follows the user across different vehicles. The car interior becomes a personalized digital space.
5) Commerce and Subscription Services
In vehicle payments and feature subscriptions allow manufacturers to generate revenue beyond vehicle sales. Certain functions can be activated only when needed, giving users flexibility while opening new business models for OEMs.
6) Over the Air Updates and Software Based Vehicles
Wireless updates improve features and performance without requiring service center visits. Vehicles are no longer finished products at delivery. They evolve continuously as software platforms.
Global Examples and CCS Market Trends
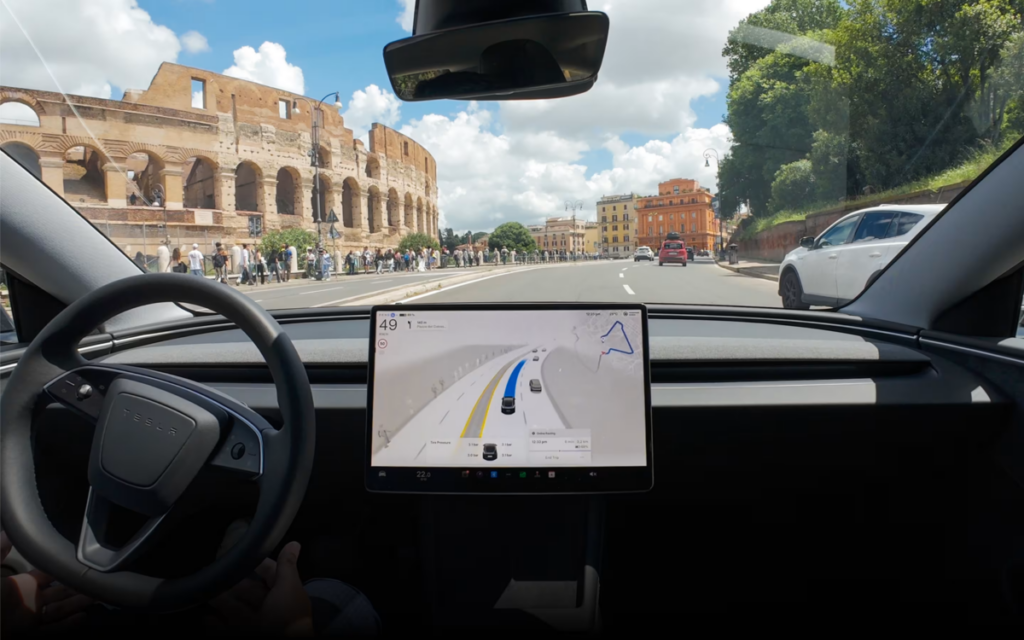

Tesla
Tesla designs its vehicles as devices that evolve over time. Over the air updates improve driving performance, battery efficiency, user interfaces, infotainment, and autonomous features. Full Self Driving is offered separately from the vehicle price and is available through subscription. Customers can activate or deactivate the service as needed. This model illustrates how software and services are reshaping revenue structures in the SDV era.

BMW ConnectedDrive
BMW ConnectedDrive integrates real time traffic and parking information, advanced maps, remote door control, vehicle location services, OTA updates, streaming applications, and the BMW Intelligent Personal Assistant. Premium digital packages are offered through subscription models. Personalized driving modes, lighting, sound profiles, and voice assistant routines strengthen BMW’s brand experience while enabling recurring digital revenue.

Hyundai Bluelink
Hyundai Bluelink allows drivers to start vehicles remotely, lock and unlock doors, locate parked vehicles, and monitor vehicle health through a smartphone app. Safety and security features include automatic collision alerts, emergency assistance, theft tracking, and real time traffic and POI information. For electric vehicles, remote charging control and battery monitoring are core functions. In several regions, Hyundai combines free trial periods with subscription transitions, demonstrating that connected services and recurring revenue models work beyond premium brands.
In addition to OEMs, technology companies such as Google, Amazon, and Microsoft provide operating systems, cloud platforms, mapping, and voice assistants for vehicles. As a result, CCS has become a collaborative ecosystem involving automakers, technology firms, telecom providers, and content companies.

Five Key Trends in the Connected Car Market
1. Transition to Software Defined Vehicles
OEMs increasingly view vehicles as centralized computing systems rather than collections of mechanical components. Distributed ECUs are being consolidated into centralized architectures with unified operating systems. This enables faster feature deployment and flexible OTA management.
2. Changing OEM Revenue Models
Revenue is shifting from one time vehicle sales to recurring income from connected services, infotainment, feature subscriptions, and data driven insurance and mobility services. The model is evolving from vehicle price plus options to vehicle plus digital subscriptions.
3. Growing Importance of Data in the Electric Vehicle Era
Battery condition, charging patterns, driving behavior, and temperature directly affect EV performance and cost. CCS enables EV specific services such as charging route optimization, battery analytics, and energy efficiency improvement.
4. Integration of Autonomous Driving and Connectivity
Autonomous driving relies on more than onboard sensors and maps. Cloud connectivity and vehicle to everything communication are essential. As autonomy advances, connected infrastructure becomes a critical foundation.
5. Expansion of AI Based Personalization
Vehicles increasingly learn driver habits, preferred destinations, content choices, and usage patterns. Personalized recommendations extend across navigation, driving assistance, maintenance, insurance, and advertising. Understanding the driver’s daily life is becoming a key competitive advantage.
What the Future Looks Like for Connected Car Services
Connected Car Service is likely to evolve beyond adding individual features. It will increasingly redefine what a car represents. Consumers may evaluate vehicles not by model year but by the software and services they use.
As autonomous and advanced driving features expand, time spent in vehicles will change in meaning. Cars are becoming spaces for work, rest, and content consumption. Listening to music during commutes, watching videos while charging, and paying for parking before arrival are becoming normal experiences.
From a business perspective, CCS enables diversified revenue models through subscriptions, data services, insurance, energy, and mobility partnerships. The automotive industry is shifting from hardware centric structures to software and service driven ecosystems that create value long after vehicle delivery.
In this context, CCS should not be seen as a technology that complicates cars. It is a transformation that makes vehicles easier to use, more valuable over time, and continuously adaptable. As electrification and autonomous driving accelerate, Connected Car Service stands at the core of the shift toward vehicles as evolving digital service platforms.
If you would like to speak directly with professionals who plan and deliver Connected Car Service, contact Liahnson & Company. We will connect you with an expert who can address your questions accurately.

Latest Posts
- Corporate Due Diligence: How to Identify Hidden Risks Behind Financial Statements
- AI in the Defense Industry: How Artificial Intelligence Is Changing Modern Warfare
- Ping An Insurance and the Future of AI Driven Insurance Transformation
- Who Is the Best ENS Company in Asia? – Why Liahnson & Company Leads the Asia Expert Network Market
- No Entry for Humans: How to Easily Understand Moltbook and Moltbot, a Bot Only Social Network Run by AI Agents
Sources
https://www.hyundai.com/kr/ko/digital-customer-support/app/myhyundai/bluelink/smart-control
https://www.bmw.com/en-au/digital-services/bmw-connecteddrive.html#digital-extensions

Leave a Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.